
Mon - Sat : 10.00 AM - 4.00PM Sunday : Closed
A maxillary nerve block is a safe, targeted injection that helps relieve pain in the upper jaw, cheek, nose, and upper lip. It’s often used to treat trigeminal neuralgia, dental pain, and facial nerve pain. By blocking pain signals from the maxillary nerve, this treatment can provide quick, lasting relief without needing strong medications. It’s ideal for people with facial pain that doesn’t respond to other treatments.
An auriculotemporal nerve block targets a nerve that affects the side of the face, temple, and ear. It’s often used to treat chronic migraines, TMJ disorders, and facial nerve pain. By stopping pain signals in this area, the injection can offer fast and long-term relief. It’s a great option if you’ve tried other headache or TMJ treatments without success.
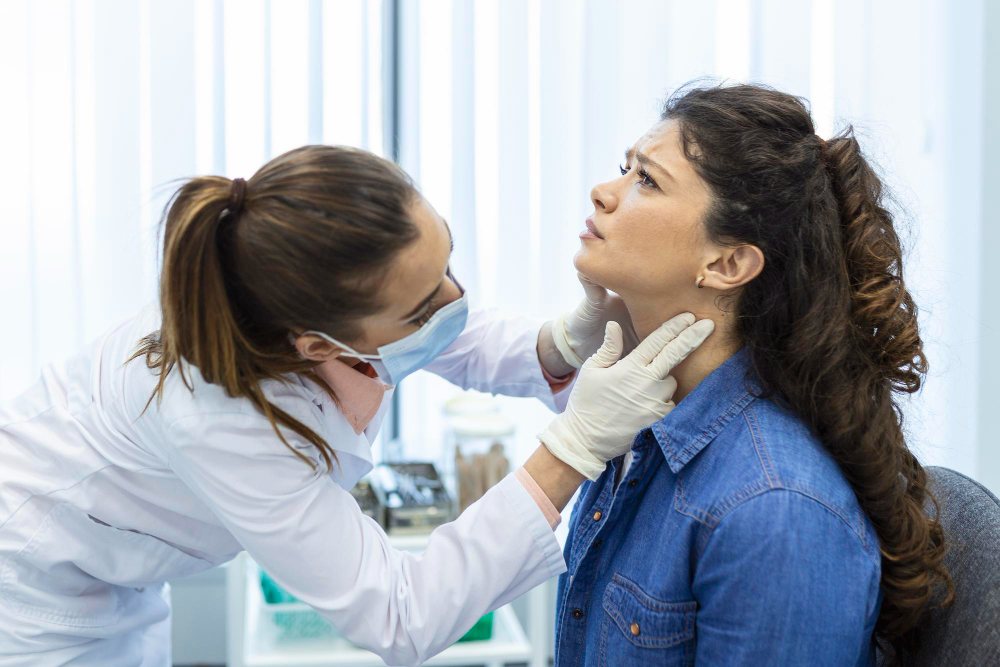
The omatrico-temporal nerve block is used for pain near the temple, eye, and upper face. This advanced injection can help reduce symptoms from nerve injuries, cluster headaches, and facial pain syndromes. It works by calming overactive nerves in this area, offering targeted pain control when other methods haven’t worked. It’s often used for complex craniofacial pain conditions.

An accessory nerve block targets the nerve that controls muscles in the neck and upper back. It’s helpful for people with neck pain, shoulder stiffness, or post-surgery discomfort. This injection reduces pain, improves range of motion, and helps you get back to your daily activities. It’s often used when physical therapy and medications alone aren’t enough.


Jacobs Pain Centre, 8920 Woodbine Ave, Ste. 102, Markham, ON L3R 9W9
Since 2002, Jacob’s Pain Centre has provided effective, comprehensive pain management through a multidisciplinary approach. We combine evidence-based treatments with supportive care to deliver accurate diagnoses and personalized pain management plans.
Copyright © 2025. All Rights Reserved.